CSL 102; Data Structures; IIIT Nagpur; Created by: Dr. Aniket Pingley
Introduction
Linked List is a linear data structure. Unlike arrays, the data in a linked list is not stored at contiguous memory locations. A linked list is created by linking the elements together. Each element in the linked list has atleast two component - 1) the data and 2) link to the next element. The first and the last elements in a linked list are typically referred as head and tail, respectively. The access to a linked list is via the head element. Traversal is performed in a strictly linear order by following the link the next element till the tail element is encountered.
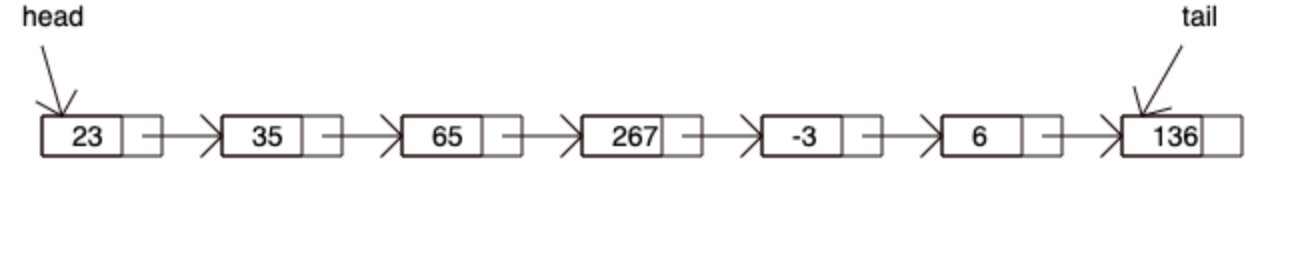
Linked List vs Array
| Array | Linked List | |
|---|---|---|
| Storage | Contiguous memory | No specific scheme |
| Memory allocation | A block of memory is allocated at once | Memory required by a single node is allocated at a given instance |
| Size | Fixed; cannot be changed at runtime | Dynamic; can change at runtime |
| Access | Via indexing | Via the head/first node and link to other nodes in linear order |
| Memory usage | Less memory required due to indexing; only data is stored | More memory is required because link to next node is stored in addition to data |
| Advantages | Less memory required due to indexing; only data is stored Random access to data possible |
Dynamic size Ease of insertion/deletion of nodes |
| Disadvantages | The size of array cannot be changed dynamically | Random access via index does not work Extra memory required to store link to the next element |
Doubly Linked List
A singly linked list does not allow access to the previous node in the list directly, thus from implementation standpoint, track of the previous node must be managed using coding logic and temporary variables. Thus, the access to nodes in reverse linear order is slow. To this end, doubly linked list is implemented where every node not just has link to the next node but also the previous one. The following figure makes the concept amply clear.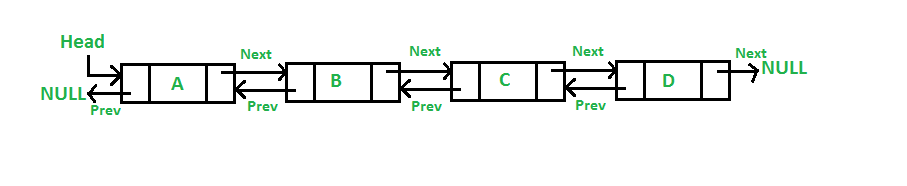 Image source: geeksforgeeks
Image source: geeksforgeeks
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Code for implementing Singly Linked List
#define EMPTYNODE 0
struct nodeQ{
short data;
struct nodeQ* next;
};
typedef struct nodeQ nodeQ_t;
typedef enum{
LIST_FALSE = 0,
LIST_TRUE = 1,
} status_t;
nodeQ_t* createNode(short val){
nodeQ_t* ptr = (nodeQ_t*)malloc(sizeof(nodeQ_t));
ptr->data = val;
ptr->next = EMPTYNODE; // NULL
return ptr;
}
status_t appendNode(nodeQ_t* tail, nodeQ_t* newNode){
if(EMPTYNODE == tail || EMPTYNODE == newNode) return LIST_FALSE;
tail->next = newNode;
return LIST_TRUE;
}
status_t prependNode(nodeQ_t* head, nodeQ_t* newNode){
if(EMPTYNODE == head || EMPTYNODE == newNode) return LIST_FALSE;
newNode->next = head;
return LIST_TRUE;
}
void printList(nodeQ_t* head){
if(EMPTYNODE == head) return;
nodeQ_t* node = head;
while(node){
printf("%d --> ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
printf("EMPTYNODE\n");
}
void destroyList(nodeQ_t* ptr){
if(EMPTYNODE == ptr) return;
while(ptr){
nodeQ_t* current = ptr;
printList(current);
ptr = ptr->next;
free(current);
}
printf("EMPTYNODE\n");
}
status_t isDataPresent(nodeQ_t* ptr, short data){
if(EMPTYNODE == ptr) return LIST_FALSE;
while(ptr){
if(data == ptr->data) return LIST_TRUE;
ptr = ptr->next;
}
return LIST_FALSE;
}
status_t insertNode(nodeQ_t* head, nodeQ_t* newNode, unsigned short index){
if(EMPTYNODE == head || EMPTYNODE == newNode) return LIST_FALSE;
if(0 == index) return prependNode(head, newNode);
nodeQ_t* curr = head;
unsigned short counter = 0;
while(curr){
counter++;
if(index == counter){
// 56
// 14 -> 16 -> 17
newNode->next = curr->next;
// 56 ->16
curr->next = newNode;
// 14->56->16>17
return LIST_TRUE;
}
curr = curr->next;
}
return LIST_FALSE;
}
status_t removeNode(nodeQ_t* head, nodeQ_t** newHead, unsigned short index){
if(EMPTYNODE == head) return LIST_FALSE;
if(0 == index){
*newHead = head->next;
free(head);
return LIST_TRUE;
}
nodeQ_t* prev = head;
nodeQ_t* curr = head->next;
// 15 -> EMPTYNODE
unsigned short counter = 0;
while(curr){
counter++;
if(index == counter){
// 15 = prev
// 16 = curr
// 17 = curr->next
prev->next = curr->next;
free(curr);
return LIST_TRUE;
}
// 15->16->17->18
// 16 = prev
// curr = 17
prev = curr;
curr = curr->next;
}
return LIST_FALSE;
}
nodeQ_t* reverseList(nodeQ_t* head){
if(EMPTYNODE == head) return EMPTYNODE;
nodeQ_t* prev = head;
nodeQ_t* tmp = EMPTYNODE;
nodeQ_t* curr = head->next;
head->next = EMPTYNODE;
while(curr){
// 15 -> 16 -> 17 -> 18 -> 19
// store curr->next into a tmp variable
tmp = curr->next;
// tmp = 17
// update next for the curr node
curr->next = prev;
// curr = 16
// curr->next = 15
// 15 <- 16 <- 17 ??? 18 -> 19
prev = curr;
// prev = 16
curr = tmp;
// curr = 17
}
return prev;
}
int main(){
nodeQ_t* head = EMPTYNODE;
nodeQ_t* tail = EMPTYNODE;
head = createNode(20);
printf("%p\n", head);
tail = head;
for(short i=1; i < 6; i++){
nodeQ_t* newNode = createNode(20+i);
if(appendNode(tail, newNode))
tail = newNode;
}
for(short i=1; i < 6; i++){
nodeQ_t* newNode = createNode(20-i);
if(prependNode(head, newNode))
head = newNode;
}
#if 0
printf("%d\t\t%p\t\t%p\n", head->data, head, head->next);
printf("%d\t\t%p\t\t%p\n", head->next->data, head->next, head->next->next);
printf("%d\t\t%p\t\t%p\n", head->next->next->data, head->next->next, head->next->next->next);
printf("%d\t\t%p\t\t%p\n", tail->data, tail, tail->next);
#endif
printList(head);
if(LIST_TRUE == insertNode(head, createNode(100), 5)){
printList(head);
}
if(LIST_TRUE == insertNode(head, createNode(101), 10)){
printList(head);
}
if(LIST_TRUE == insertNode(head, createNode(450),20)){
printList(head);
}
if(LIST_TRUE == removeNode(head, &head, 8)){
printList(head);
}
if(LIST_TRUE == removeNode(head, &head, 0)){
printList(head);
}
if(LIST_TRUE == removeNode(head, &head, 800)){
printList(head);
}
head = reverseList(head);
printList(head);
//printf("dataPresent = %d \n", isDataPresent(head, 225));
//destroyList(head);
//head = EMPTYNODE;
//printf("%d\n", head->data);
return 0;
}